The BF data sheets – which list representative Psi-values for windows and for façade profiles – published by the Bundesverband Flachglas e.V. (“BF” = German Federal Flat Glass Association) are often used to determine UW– and UCW-values. This comparatively simple (but standard-conforming) method is well known in the market – far beyond the borders of Germany. A new project of the BF “Warm Edge” Working Party now aims to permanently ensure trustworthiness and reliability of the declared values.
The representative Psi-values of the BF data sheets for windows and for façade profiles are calculated according to EN 10077-2 using the so-called equivalent thermal conductivity λeq,2B, (which is determined by measurement). The basis for this approach, as well as for the validity and application of these representative Psi-values are the three ift guidelines about thermally improved spacers, namely WA-08, WA-17 and WA-22. To declare the value of λeq,2B, three pairs of test specimen made from desiccant-filled and butyl-equipped spacers are measured, followed by a statistical evaluation. The value is shown on the BF data sheets on the bottom under ‘Two Box model Characteristic values’ in ‘Box 2’.
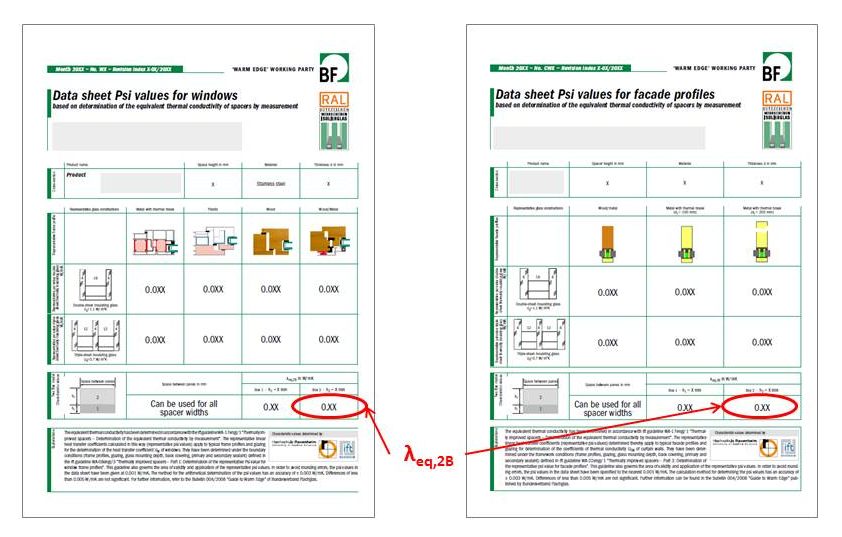
Picture: In the future, the value λeq,2B, declared on the BF data sheets shall be rechecked on a regular basis. The value is not suitable for a comparison of individual thermal performances of warm edge systems. For that purpose, only the indicative Psi-values shall be used, because they also include the influence of the spacer height h2.
Apart from a few exceptions, the sole difference in calculating warm edge systems are the input data λeq,2B and the height h2 of the spacer box 2. Therefore, the value λeq,2B is particularly important. It determines the Psi-values which are the most important performance factors of spacer manufacturers in their daily competition.
Consequently, during their last meeting on February 9th, 2017, the members of the BF “Warm Edge” Working Party have agreed a voluntary commitment to scrutinize the equivalent thermal conductivity values λeq,2B every two years. This shall allow the detection of any deviations compared with the original measurements, and as an additional benefit will provide the security that the values declared on the BF data sheets are still correct. The costs of the procedure will be borne by the respective spacer manufacturers.
The measurements shall exclusively be made by ift Rosenheim. It is worth emphasizing that the samples for these check measurements shall be collected from the spacer processing companies in the market, and not supplied by the spacer manufacturers themselves.
From 1st of January 2017, the RAL Gütegemeinschaft Mehrscheiben-Isolierglas e. V. (“GMI” = German Multi-Pane Insulating Glass Quality Association) has already implemented an external monitoring of the insulating glass components spacer, sealants and desiccant. It aspires to later include the control of λeq,2B, planned to be done every two years, into the ‘RAL-GMI Quality monitoring and testing standards for multi-pane insulating glass’.
As of the first re-measurement, the currently valid BF data sheets, available online on the BF websites, will be equipped with an expiration date of validity. The first check and new dating of the data sheets shall take place in 2018.
The „Warm Edge“ Working Group
The ‘Warm Edge’ working group is a subcommittee of the Technical Committee of Bundesverband Flachglas. The participants in the working group are members and sponsoring members of BF. Scientific support for the working group is provided by Prof. Dr. Franz Feldmeier, Rosenheim University of Applied Sciences and by Mr. Norbert Sack, ift Rosenheim.
This is a press release of BF Bundesverband Flachglas and ift Rosenheim of March 2017


Letzte Kommentare: